Treatments of leg veins in men and women does not differ, however, the frequency of postoperative recurrence in women above in connection with the additional influence of hormones (estrogen effect).
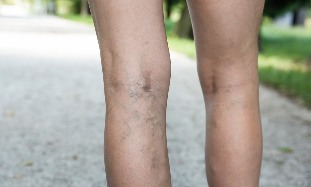
Venous disease of the legs needs to be treated by a doctor-phlebologist, who is engaged in this pathology. The various treatments for varicose veins are not radical, since they are not aimed at addressing the main pathogenetic causes of the failure of the valve apparatus veins. Surgical and conservative treatment delay the progression of the disease for a long line. The percentage of recurrence is high ranging from 10 to 50% 5 years after surgery.
Treatment of varicose veins should be comprehensive. There are three groups of methods of eliminating varicose veins:
- surgical,
- conservative.
Each treatment has its advantages and disadvantages, a certain frequency of recurrence. The choice of method is arbitrary, so considering how to achieve the most favorable outcome often combine all three methods.
The typical symptoms of varicose veins in women
Common manifestations characteristic of women
The symptoms of varicose veins begins with the occurrence of such functional disorders as a feeling of heaviness in the legs, swelling of the ankle joints to the end of the day. On the skin of the legs is first formed spider veins.
The main signs of the disease – Association of varicose saphenous veins, within a few years of onset.
If untreated at this stage, causes such symptoms as cramps in the calf muscles, itchy skin on the feet.
Signs of venous disorders: pigmentation of skin in the lower third of the leg, cyanosis, sclerotic changes of the subcutaneous tissue, eczema, trophic ulcer is formed.
The typical symptoms of varicose veins in females
- The painful symptoms appear cyclical, worse before menstruation, due to changes in levels of sex hormones;
- during pregnancy resulting symptoms of varicose veins after birth may disappear;
- in the second half of the menstrual cycle because of the action of progesterone, the diameter of the varicose veins increases, so the symptoms of swelling and heaviness in the legs, more pronounced;
- symptoms of varicose veins worsen during hormone therapy.
Now let's talk about the methods of therapy.
The best methods of treatment
Radiofrequency ablation and laser photocoagulation
Radiofrequency ablation of veins
The method is based on the introduction of ultrasound under the supervision of a special disposable catheter into the lumen of the expanded veins.

The catheter is equipped with a special electrode, the working of which under the action of RF radiation heats up to 120 degrees. Advancement of the catheter through the veins leads to bonding the vascular wall. Off the affected vein from the circulatory system of the legs.
Venous laser photocoagulation
Surgical technique consists of puncture of the affected vein and introduction into its lumen under ultrasound guidance a laser fiber. Under the action of laser radiation occurs, the coagulation proteins of the vascular wall, causing Vienna to subside and after some time, overgrown connective tissue.
Radiofrequency ablation and venous laser ablation are relatively new methods of treatment of varicose veins on the legs. Despite the differences in technique, have common characteristics.
The advantages and disadvantages of radiofrequency ablation and laser venous ablation
Advantages:
- Do not require hospitalization;
- Speed of execution (from 30 min to 1 hour);
- Painless;
- Bloodless;
- Performed under local anesthesia;
- The lack of postoperative scar (for women desired cosmetic effect);
- Short term rehabilitation.
Disadvantages:
- High price;
- The frequency of recurrence to 10%;
- The inability of the procedure and some anatomical peculiarities of the veins (severe tortuosity of vessels).
Radiofrequency ablation and venous laser ablation choose women who want to treat varicose veins in an outpatient setting with minimal restriction of physical activity in the postoperative period and preserving the aesthetic appearance of the legs.
Fleboskleroterapija
In the lumen of the affected segment of the vein injected a special drug that has a specific effect on the vascular wall. Sclerosing agent may be used in liquid form or in the form of foam. Preference should be given foam sclerotherapy due to a larger area of contact of the substance with the wall of the vein.
The advantages and disadvantages of Fleboskleroterapija:
- The lack of postoperative scar;
- Performed on an outpatient basis;
- The operation is performed without anesthesia;
- Manipulation is virtually painless (slight stinging at the puncture site);
- Possible long-term pigmentation of the skin at the puncture site (up to 2 years);
- In rare cases, postoperative inflammation of a vein (phlebitis);
- Swelling and redness of the tissues within 2 days after the procedure;
- Allergic reactions are hypersensitive to the drug;
- In 20% of cases have spider veins on the legs (telangiectasia);
- The frequency of recurrence to 50%.
Recurrence of varicose veins after sclerotherapy depends on the lumen of the affected vessel: the wider the clearance, the higher the risk of recanalization in it. Choose this therapy in the treatment of recurrent varicose veins after surgical phlebectomy.
Surgical phlebectomy
Surgery is a more radical way to eliminate varicose veins. Principles of surgical treatment are the elimination of abnormal discharge of the blood from deep into superficial veins of the legs and removal of the blood vessels themselves. Stages combined phlebectomy:
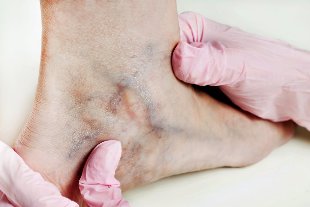
- Crossing and ligation of the mouth of the great saphenous vein (incision in the groin) or small saphenous vein (incision in the popliteal fossa);
- Remove stems of varicose veins. By using a special metal probe which draws the vein into the skin incision.
Advantages:
- Radical;
- The ability to perform operations at any stage of the disease.
Disadvantages:
- Hospitalization of 5 to 7 days;
- The scar in the legs;
- Spinal anesthesia or General;
- Injury to the surrounding tissue upon pulling out the vein;
- Possible complications: bleeding, wound infection;
- The recurrence rate to 20%.
To be treated surgically, preferably with a certain type of lesion occurs when varicose deformity of the great or small saphenous veins to a considerable extent. And also when there are signs of trophic disorders of soft tissues and symptoms of decompensation of the venous insufficiency.
Miniflebjektomija
Miniflebjektomija – a separate option of surgery, which can treat varicose veins of the legs in the initial stages. Often used in the presence of a single varicose nodes on the shins. Performs skin puncture on pathological education and with a hook in the sky, and crossed Vienna. Operation does not require General anesthesia and dermal suturing.
Conservative therapy
Begin to treat the varicose disease in the legs is necessary with use of drug and compression therapy. The purpose of the preparations improving blood circulation and wearing medical compression hosiery – main conditions that determine the outcome of any surgery on the veins of the legs.
Drug therapy
Medications these medications stop the symptoms of venous insufficiency, are used as a preoperative preparation and postoperative rehabilitation.
Treated with special preparations varicose veins on the legs takes a long time in a continuous mode or in repeat courses.
Compression therapy
Elastic compression leg – a leading method of treatment in cases where surgery is contraindicated. As the compression means you can use elastic bandages and special medical hosiery: stockings, socks, tights. Medical products feature high strength, long time retain the original compression level, comfortable to wear, which is important for women.
There are 4 classes of elastic knitwear depending on the degree of compression. Recommended to treat the varicose veins with the use of the goods class 2 in the absence of disease progression up to 6 months and with continued use during exercise or during prolonged stay on their feet. If there are signs of damage to the valves of deep veins or severe symptoms of impaired lymphatic drainage, there shall be jerseys class 3 to stop the progression of varicose veins.
Therapeutic effect of compression hosiery is due to:
- the decrease in the veins, resulting in less discharge of blood in the varicose vessels;
- increased intake of tissue fluid into the blood stream, so the signs of puffiness and the symptoms of heavy legs disappear;
- improvement of fluidity of the blood, which prevents blood clots.



































